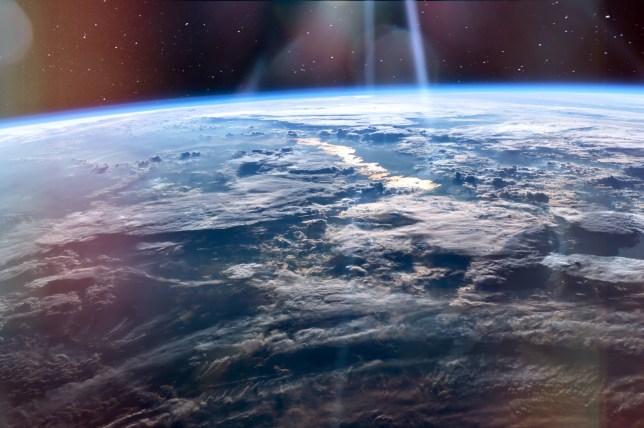
A hole in the ozone layer over Antarctica is healing and in turn, reversing changes it caused to the flow of winds over the southern hemisphere, a study discovers.
Researchers from the University of Colorado Boulder say this is due in part to a ban on ozone-depleting substances (ODS) in the 1980s.
The biggest impact can be seen in the southern hemisphere jet steam – it had been moving further south due to ozone depletion, but that appears to be reversing.
Antara Banerjee, lead author, says this is likely only a temporary change due to the impact of rising carbon dioxide levels and more ODS coming from China.
Before 2000 the mid-latitude jet stream had been gradually shifting towards the South Pole and another hurricane-causing jet stream was getting wider.
This was changing rainfall patterns and ocean currents in the southern hemisphere and causing countries like Australia to suffer severe drought.
Researchers used a range of computer simulations to show the jet stream stopped moving south at the same time as the ozone hole.
began healing.
In Australia changes to the jet stream led to an increased risk of drought by pushing rain away from coastal areas.
If the jet stream reverses its southwards movement it could bring those rains back to the country.
Last year the Antarctic ozone hole hit its smallest annual peak on record – since it was discovered in 1982 – but it’s a temporary fix.
Scientists say this may be due to unusually mild temperatures in that layer of the atmosphere.
There has also been a surge in ozone-depleting chemicals coming from industrial regions of China, the team confirmed.
‘We term this a “pause” because the poleward circulation trends might resume, stay flat, or reverse,’ says Banerjee.
‘It’s the tug of war between the opposing effects of ozone recovery and rising greenhouse gases that will determine future trends’
She said the biggest discovery from their study was proof that a global protocol like the one in Montreal that banned ODS can pause or reverse environmental harm.
The study was published in the journal Nature.
What's happening in Tunisia?
Subscribe to our Youtube channel for updates.